Skin cancer is America’s most common cancer, with over 5 million cases diagnosed in the United States each year.
We’re here to acknowledge May as Skin Cancer Awareness Month, talk about how skin cancer can be prevented, and go over some tips that can be helpful when protecting your skin. We also encourage you to learn about the dangers of unprotected sun exposure, as this is the most common way one can get skin cancer.
How does the sun affect the skin and cause cancer?
Significant damage can be done to the DNA in our skin cells when the skin is exposed to too much ultraviolet (UV) radiation, either from the sun or tanning beds. Enough DNA damage over time can cause cells to grow out of control which can ultimately lead to skin cancer. It’s important to remember that skin damage doesn’t only happen on hot or sunny days.
There are 2 main types of UV rays. Both types can damage our skin and cause cancer.
- UVB reaches the outer layer of the skin (the epidermis) and causes most sunburns.
- UVA reaches deeper into the inner layer of the skin (the dermis). It is responsible for aging the skin but contributes less to sunburns.
How can I protect my skin from dangerous sun exposure?
There are A LOT of SPF products on the market today, and finding the right one that will be the most effective is crucial. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends choosing a sunscreen that says:
- Broad spectrum: The words "broad spectrum” means that the sunscreen can protect your skin from both types of harmful UV rays — the UVA rays and the UVB rays.
- SPF 30 or higher: The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that you select a sunscreen with an SPF rating of 30 or higher.
- Water resistant: Dermatologists also recommend that you look for the words "water-resistant.” This tells you that the sunscreen will stay on wet or sweaty skin for a while before you need to reapply. Water resistance lasts either 40 or 80 minutes. Not all sunscreens offer water resistance.
Other ways I can protect my skin
- Sunscreen alone cannot fully protect you. In addition, seek shade and wear sun-protective clothing, including a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses, whenever possible.
- Avoid tanning beds at all costs. Indoor tanning can increase the risk of developing melanoma by 47%, and the risk increases with each use.
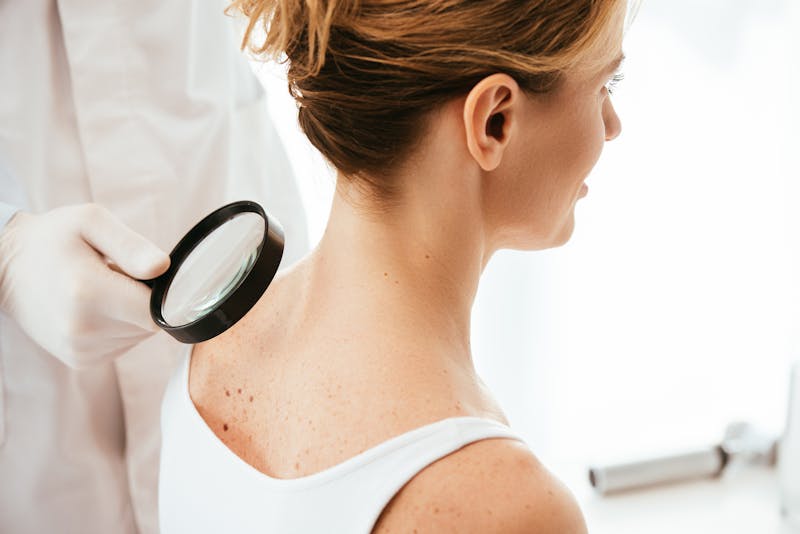
- See your Dermatologist regularly for skin exams. Especially if you notice a new mole or notice changes in an existing mole, and never ignore any irregular skin concerns, it’s always best to schedule an appointment right away. It could save your life.


